🍎 Apple's Latest AI Features for Students
Apple recently released the launch of Apple Intelligence, a suite of AI features that may revolutionize education
Most recently, Apple introduced its own personalized AI system called Apple Intelligence. At the latest WWDC 2024, they showcased a series of AI features powered by generative models that will be integrated into iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia. They released features such as the ability to learn and copy the user’s unique handwriting, perform automatic calculations to solve math problems, summarize chunks of text, and many more. Apple Intelligence also includes advanced tools that can generate full emails and custom images. As generative AI becomes more incorporated into our everyday devices, the importance of educating the future generation about AI is more apparent than ever. In this newsletter edition, we will explore some of these AI features that have the potential to significantly impact students and educators alike. As we gear up to revamp our newsletter throughout the summer, we welcome your feedback to help us improve! What is your favorite section of the AI x Education newsletter?
Here is an overview of today’s newsletter:
New AI Features with Apple Intelligence
Youth Perspectives on Gen AI Across Various Racial and Ethnic Groups, Ages, Gender Identities and More
Results from Study on the Learning Outcomes of Utilizing LLMs
The Realities and Limitations of GPT-4o
🚀 Practical AI Usage and Policies
Apple has recently introduced new AI features that students and educators can leverage to enhance their learning and teaching experiences. Here is an overview of some key features:
Math Notes
The new iPadOS 18 Calculator app and the Notes app both offer a powerful feature called Math Notes. This feature allows users to write down mathematical expressions and problems just like they would on paper using their Apple Pencil. As soon as they write an equal sign (=), the app automatically solves the calculation and displays the answer in their own handwriting.
Math Notes goes beyond simple calculations. It also supports variables. Users can assign values to these variables and see how the final answer changes in real-time. This is particularly helpful for understanding how variables impact equations in subjects like math and physics.
Additionally, Math Notes allows users to generate graphs of their equations with a single tap. Users can add multiple equations to the same graph to visualize the relationships between them. This graphical representation could provide a deeper understanding and intuition of mathematical concepts.
To see Math Notes in action, check out this video here.
Smart Script
Smart Script is a new feature in the Notes app that significantly enhances the handwriting experience. This feature utilizes a machine learning model to analyze your existing notes and learn your unique handwriting style. As you write with your Apple Pencil, Smart Script refines your strokes in real-time, making your handwriting smoother, straighter, and ultimately more legible.
Smart Script offers additional functionalities that streamline note-taking. You can seamlessly paste typed text into your handwritten notes, and it will automatically convert it to match your handwriting style. It can also conduct spell checks and change the spelling of your personal handwriting style. While this feature makes it easy for students to take quick handwritten notes, it might pose a concern for educators who require authentic handwritten work, as students could paste text that mimics their handwriting.
To see Smart Script in action, check out this video here.
In other news, OpenAI recently released ChatGPT Edu, a version of ChatGPT specifically designed for universities. Here is the link to more information. They provide a more accessible option to bring AI to campuses at scale. ChatGPT Edu is powered by GPT-4o and offers advanced tools such as data analysis, document summarization, code assistance, and more.
When it comes to implementing AI, Sal Khan, CEO of Khan Academy, shares his insights on important considerations when incorporating AI tools into classrooms and school districts. Here is the link to the LinkedIn post. He also recently released a book called Brave New Words: How AI Will Revolutionize Education (and Why That's a Good Thing) that shares the potential of AI in transforming education.
📣 Student Voices and Use Cases
Hopelab, Common Sense Media, and the Center for Digital Thriving at the Harvard Graduate School of Education recently collaborated on a study and released a report titled Teen and Young Adult Perspectives on Generative AI. This report explores the varying experiences and perceptions of generative AI among different racial and ethnic groups, comparing teens (ages 14-17) and young adults (ages 18-22), as well as examining differences across LGBTQ+ and gender identities.
Here are some key statistics shared in the report:
Approximately half (51%) of teens and young adults ages 14-22 say they have used generative AI tools at some point, with just 4% reporting daily usage
While similar percentages across demographic groups have tried generative AI, Black and Latinx youth are twice as likely as white youth to use it weekly (22% and 18% vs 10%)
Most students used generative AI for getting information (53%) and brainstorming (51%)
41% of teens and young adults believe generative AI will have both positive and negative impacts on their lives in the next decade. 19% percent anticipate mostly negative impacts, with LGBTQ+ youth almost twice as likely as their cisgender/straight peers to feel this way (28% vs 17%)
About one-third (34%) of those who have never used generative AI think it would not be helpful to them
Below are quotes from students who have shown excitement for AI:
"Generative AI helps to give ideas when I need a topic to write about or to help in finding the answer to a math or chemistry problem that a traditional math app cannot solve"
"Tools like ChatGPT could be useful for writing essays in the future not to write entire essays, but to help with the outline of one"
"I think that it [generative AI] will revolutionize efficiency at school and in the workplace, freeing up workers for higher-level activities. To me, AI is just as significant of an invention as the Internet was"
"AI is not scary for me," explained one Latinx nonbinary teen, "I use it to help me compose reports, build lists, plan days, fact check, and have conversations."
"AI can be a helpful tool, like Google in the way it can help you search and even research things!"
"[Teens] use [AI] for good purposes"
Below are quotes from students who have expressed concerns about AI:
"I think that it will outperform human tasks and there will be less jobs"
"As an artist, I worry that many companies who would usually contract real artists will switch to lower quality AI-generated content to cut corners and save money"
"It will get too advanced on its own for humans to have control over it"
"I'm worried about it stealing art from artists I'm worried about it being used to generate slanderous material"
"It is a tool that can be used for both beneficial and malicious purposes"
"Sometimes it's not healthy and sometimes it is very beneficial. It's very confusing"
"AI is very creepy. AI concerns me"
Hopelab, Common Sense Media, & the Center for Digital Thriving. (2024). Teen and young adult perspectives on generative AI: Patterns of use, excitements, and concerns. Common Sense Media.📝 Latest Research in AI + Education
Stanford University
This study explores the introduction of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 in an online coding class of 5,831 students from 146 countries. The study found that while the availability of GPT-4 improved exam performances for those who used it (adopters), it overall decreased student engagement in the course, including lower participation in exams, homework, and sections.
This research underscores the complex impacts of integrating AI tools like GPT-4 in educational settings. While LLMs can enhance learning outcomes for users, as indicated by the adopters' improved exam scores, their presence might also diminish overall student engagement. This effect was particularly pronounced in students from higher HDI countries, contrasting with increased engagement from students in lower HDI regions. The research highlights the need for further investigation into the effects of LLMs in education, especially considering the long-term implications for student success and engagement.
Nie, A., Chandak, Y., Suzara, M., Ali, M., Woodrow, J., Peng, M., … Piech, C. (2024, April 25). The GPT Surprise: Offering Large Language Model Chat in a Massive Coding Class Reduced Engagement but Increased Adopters Exam Performances. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qy8zdGoogle, UC Berkeley
Children's Mental Models of Generative Visual and Text Based AI Models ↗️
This paper investigates how children aged 5-12 form mental models of generative AI models, focusing on text-based systems like ChatGPT and visual-based systems like DALL-E. The study surveyed and observed over 40 children, revealing that children generally view AI positively and are enthusiastic about how AI can assist them in daily activities. Children associated AI with positive adjectives rather than negative ones and demonstrated a preference for imaginative tasks, particularly with visual-based AI models, showing a distinct use pattern compared to text-based models.
The study highlights that children's mental models of AI are dynamic and evolve with interaction. Children do not perceive AI as human-like or capable of human emotions such as getting upset, but their engagement with AI leads to a friendlier perception over time. This research underscores the need to further explore how children understand and interact with AI technologies, suggesting that future AI tools should be designed considering these evolving perceptions to ensure they are beneficial and appropriate for young users. The ongoing research aims to deepen understanding of these models by expanding the study to a larger group and examining more nuanced aspects of children's perceptions of AI.
Kosoy, E., Jeong, S., Sinha, A., Gopnik, A., & Kraljic, T. (2024). Children's mental models of generative visual and text based AI models. *arXiv*. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2405.13081📰 In the News
The New York Times
The New ChatGPT Offers a Lesson in A.I. Hype ↗️
Key takeaways:
OpenAI released GPT-4o, an update to their ChatGPT series, with advertised features like a more human like voice and real-time problem-solving capabilities. However, the actual launch lacked many of these features, with only photo uploads for analysis and standard responses included.
For instance, for a geometry problem on intersecting triangles taken from the SAT, the model understood the question but gave a wrong answer. Similarly, the bot made multiple logical mistakes on a physics problem taken from the AP exams.
Some of the hyped features such as the improved voice and video camera analysis were delayed for further fixes. Moreover, a previously introduced voice, likened to actress Scarlett Johansson, was removed following legal concerns.
Despite the limited rollout, the updated chatbot showed some improvements, like faster and clearer responses and real-time language translation capabilities, but it struggled with complex math and physics problems and demonstrated minimal improvement in reasoning abilities, casting doubt on its effectiveness as a reliable tutor.
Texas Tribute
How Texas is preparing higher education for AI ↗️
Key takeaways:
Texas colleges are actively preparing for the integration of AI in education by establishing new programs and colleges focused on AI, cybersecurity, computing, and data science. For example, the University of Texas at San Antonio is planning to launch a new college by fall 2025, aiming to equip students with AI competencies demanded by future employers.
Some institutions, such as the University of North Texas and the University of Texas at Austin, have introduced graduate programs and certificate courses in AI. Houston Community College has initiated a bachelor's degree program in AI and robotics, reflecting a trend toward making AI education more accessible and inclusive.
The approach to integrating AI in Texas education emphasizes collaboration between educational institutions, industries, and students to ensure that educational content remains relevant and that faculty and students are prepared to use AI effectively in the workforce. This collaborative effort aims to prevent institutions from working in isolation and duplicating efforts in AI education.
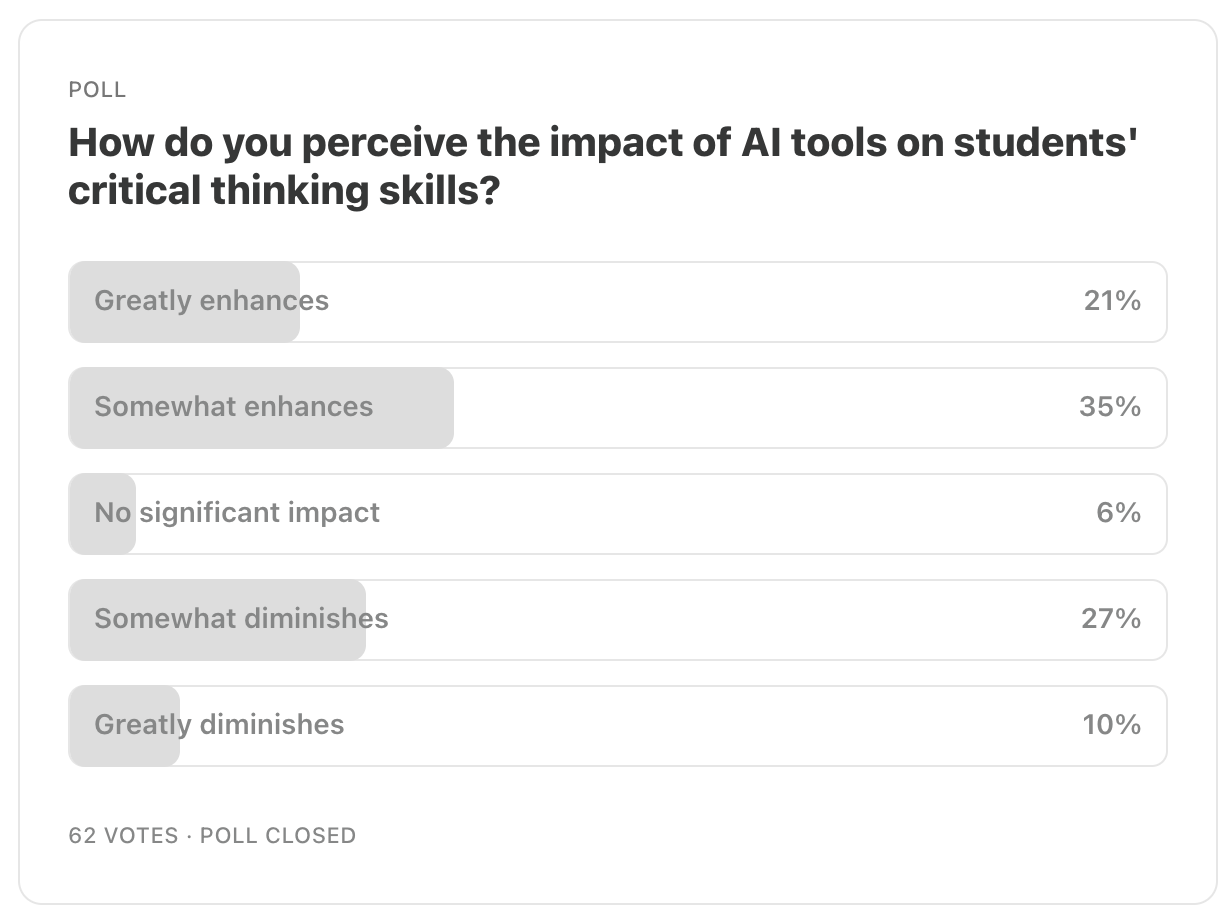
“Chatgpt.” ChatGPT, OpenAI (GPT-4), openai.com/chatgpt. Accessed 12 Jun. 2024. And that’s a wrap for this week’s newsletter! Based on our previous poll, we noticed that our readership was roughly halfway divided on AI tools either enhancing or diminishing critical thinking skills, with a slightly higher percentage finding they enhance critical thinking abilities. We encourage you to join the conversation by sharing your observations on how AI tools have influenced students in your educational settings in the comment section below.
If you enjoyed our newsletter and found it helpful, please consider sharing this free resource with your colleagues, educators, administrators, and more.